Data mapping is a crucial design step in data migration, data integration, and data transformation projects. Modern-day data mapping solutions leverage artificial intelligence (AI) to map data fields from a source format to a target format. Consequently, business users can establish relationships between separate data models from disparate sources or systems. This enables companies to facilitate improved business analysis, forecasting, and decision-making. So, data mapping is not only important for data integration processes but also for the growth of a business.
Why Is Data Mapping Important for Business?
Every organization handles vast amounts of data from multiple sources, often in various formats. This diversity makes it challenging to integrate the data into a unified database for analysis. This is where data mapping comes in. It helps business users quickly map data, enabling smoother integration for further analysis and use.
Data mapping in its simplest terms is to map source data fields to their related target data fields. For example, the value of let’s say a source data field A goes into a target data field X. Data mapping solution enable developers to code these conversion rules to achieve the expected target output.
Contact Us
Get in touch to discuss your integration needs.
Applications consist of underlying metadata that provides information on the individual data objects, attributes, fields, and business or semantic rules on how this data is persisted in its data repository. For example, Salesforce.com has a data object called Accounts and its schema consists of fields, attributes, enumerations, data integrity and dependency rules with other data objects. Therefore if there is a need to add or update a new data record from another application into the Accounts data object then there is a need to create a data map between the incoming data into the Salesforce.com Accounts format.
The complexity of data map varies from the type of hierarchical data structure that the source or target schema represents to the complexity of conversion rules that the target application requires for successful data integration. Also the mapping can be between multiple sources and targets where the data from two or more sources need to be merged or joined prior to mapping the result to the target.
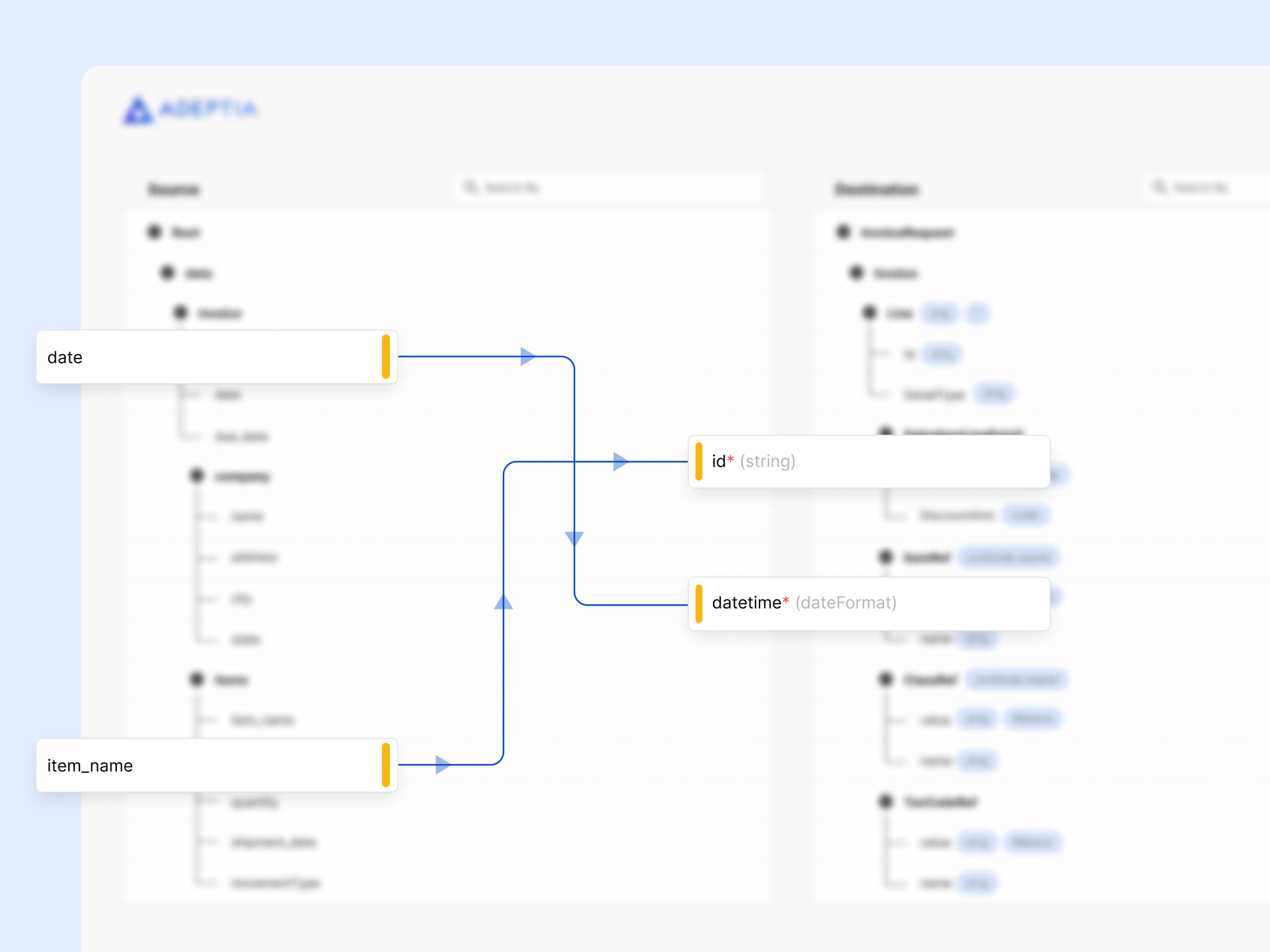
What Are the Capabilities and Features of Data Mapping?
Here, I’m going to present Adeptia’s AI-powered data mapping capabilities which I think are unique in the market in terms of the breadth of features it supports out-of-the-box and the ease of implementing the mapping rules without having to write custom code. It uses machine learning for inferring data mapping predictions from an existing library of tested data maps, reducing the effort and time to create intelligent data mappings. Its transformative features like improved strength, browser-based access, drag-and-drop mapping features, superior built-in functions, and more have made this data mapping the front-runner. You can see a demo of Adeptia Connect to try these data mapping steps on our live platform.
See Adeptia in Action
Schedule a personalized demo and discover how Adeptia can help you move faster, work smarter, and scale with confidence.
So let’s first begin by discussing the basic feature strength which is that it is completely browser-based. All you need is a browser to invoke the mapper interface and it opens up on your machine. No need to install a thick client on your desktop to access this interface. Now the advantage of its browser-based access is also that you can access it from anywhere through your secure cloud or on-premise Adeptia login. And if you are part of a user group with sharing rights with the rest of your team, you can collaborate with other users to contribute or assist in your data mapping activity. The speed of creating data maps is no longer restricted to a single developer, now with this collaborative platform your team of business users and developers can work together and create data maps quickly and speed up the time it takes to onboard data into your applications.
With its drag-and-drop mapping, the mapper interface can be used by non-technical users. Simply click and drag a source field onto a target field and your data mapping is done. And if there is a need to apply additional rules on the map then use the built-in functions to transform the data as per your business rules. Built-in functions include math, string, conditional, code conversions, and database or reference lookups. Users can also call external programs, database-stored procedures, and web services.
Below is a short list of key features which I think are important in understanding the type of features you should be looking for when evaluating a data mapping solution:
With enterprise data becoming more diverse and voluminous, the need for businesses to leverage data and transform it into valuable insights has become more important than ever. Prior to extracting value out of such diverse data, organizations need to unify and transform it into a format suitable for operational and analytical processes. This relationship-building between various data models is accomplished through AI-enabled data mapping, which is an integral step of data management.
There are many additional features that we would like to show you in a live demo and also walk you through your use case and build out a map in a live session.
Steps of Data Mapping
Data mapping is a crucial process in ensuring that data is accurately and consistently transferred from one system to another. The steps involved in data mapping include understanding the source and target systems, identifying the data elements that need to be mapped, determining the mapping rules and transformations, creating a mapping document, and validating the mapped data.
Firstly, it is important to thoroughly understand the source and target systems, including their data structures and formats, to identify any potential mismatches or incompatibilities. Next, the specific data elements that need to be mapped are identified, considering the differences in naming conventions and data types. Mapping rules and transformations are then determined, specifying how the data will be converted or manipulated during the mapping process. A mapping document is created to outline the data mapping rules, serving as a clear reference for developers and analysts involved in the process.
Finally, the mapped data is validated to ensure its accuracy and integrity, and any discrepancies or errors are resolved before the data is transferred to the target system. Overall, the steps involved in data mapping are essential in ensuring a successful and reliable data transfer process.