Software solution vendors in the Health Care industry provide a key function in connecting customer data with the Insurance Carriers (Payers). Member enrollments generated from a State’s public Healthcare Integration requires HIPAA validations, data enrichment and data transformation before the information is sent out to the Payer. Thus the function that these brokers perform facilitates the process of enrolling consumers into their selected health care plans quickly and also helps Payers to onboard new customers into their Insurance products. The result is faster revenue for Payers and affordable health care plans for customers.
One of the ways Adeptia Solutions can be used by the solution vendors is to use our product as an Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) that takes the inbound EDI 834 and routes it through different steps of decryption, HIPAA validation, data transformation, and ultimately into a canonical format that can be then sent out to the Payer.
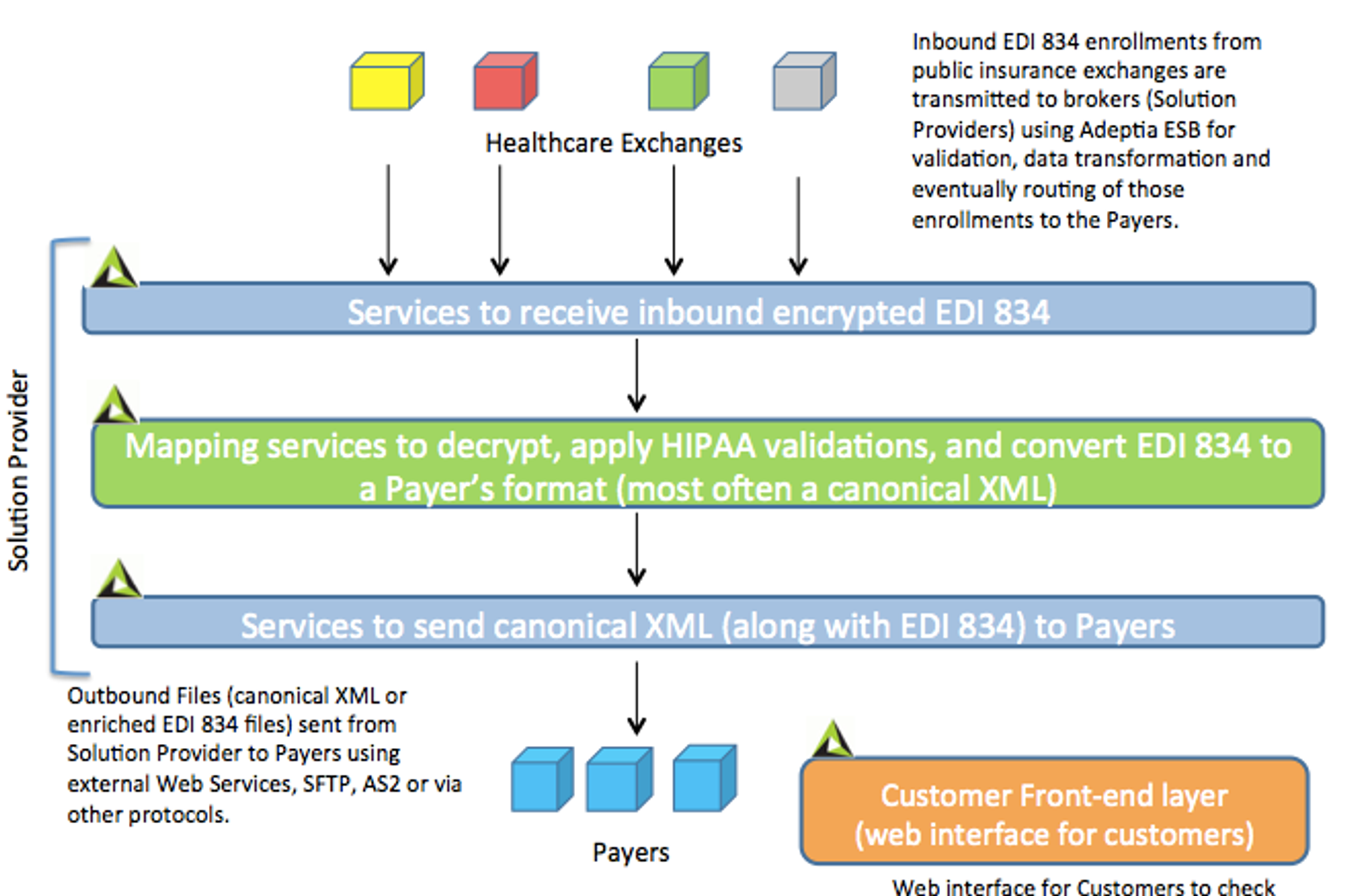
So we have put together a high-level architectural diagram of where Adeptia fits in the EDI 834 integration process.
Notes on some of the best practices in implementing an ESB architecture:
- Having a Services layer would allow you to manage the underlying flows without affecting how the EDI 834 files are transmitted.
- Similarly, the data schemas of the inbound EDI 834 and outbound Payer’s canonical formats do not need to be changed as you modify your underlying business processes over time. A smart ESB product should be code-free and meta driven. Idea is once you define your schemas and maps there is very little to do in terms of modifying these objects further over time. Only time you would make the changes to the schemas is when you have changed in the EDI 834 version (for example moving from version 4010 to 5010) or there’s an update in the Payer’s output format.
- Services layer primarily consists of web service SOAP or REST APIs, decryption services, data validation services, mapping services, and meta-data of Schemas and business rules that are applied on the EDI 834 files at run-time. Here’s an example ofAdeptia’s Claims onboarding solution.
- Consider creating ‘templated’ process flows to handle the common steps of data transformation and routing where the behavior of the process is determined by the type of data being received from Source. For example, if a State sends an EDI 834 that requires specific handling in mapping then that particular map can be applied at runtime dynamicallybased on which State or marketplace is sending that file. Thus the need to create individual processes for each health care exchange is not needed.
- Meta-driven and not a code based ESB is key to rapidly scale your solutions as you add more value-added services into the solutions you are offering to the State healthcare exchanges, Healthcare Providers or Payers.
- Have your business users be able to graphically map the EDI 834 to Payer’s format. Graphical data mapping and validation would allow your business analysts be able to onboard new customers into your service without having to hire expensive developers.
- SOA approach of re-using template mapsfor new customers is important so that your team is not creating new maps from scratch every time a new customer or Payer is added into your service.
- ESB should have web-forms and dashboard capability to allow enrollees to check the status of their enrollment and claims applications.